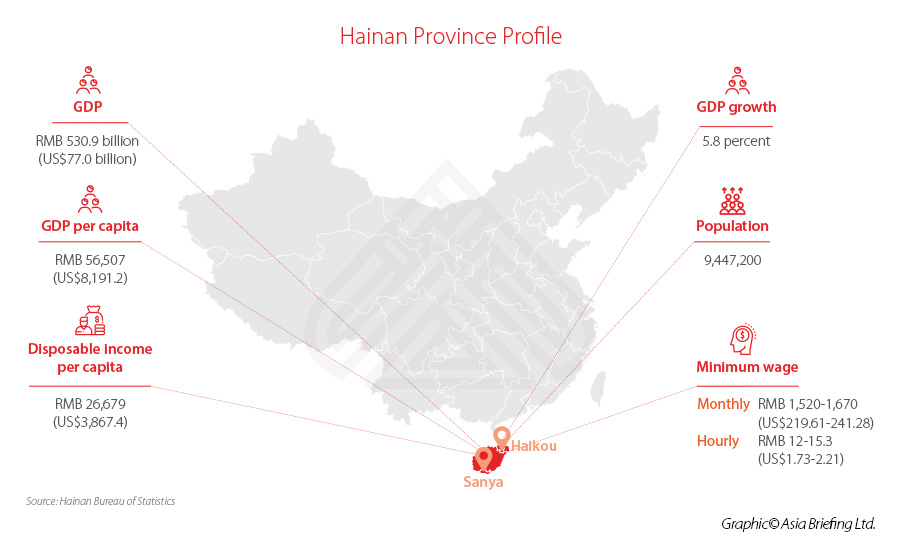
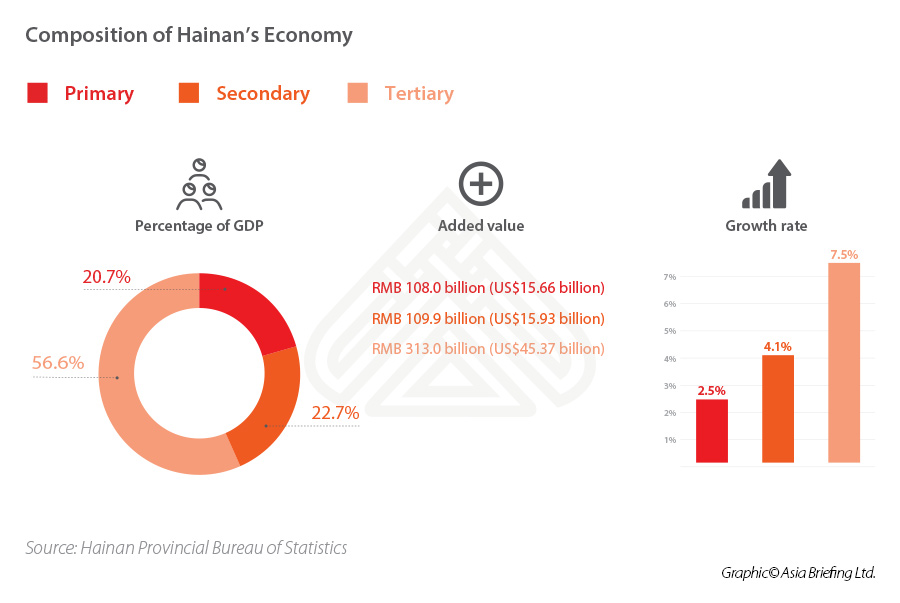
On June 10, 2021, China passed a law on the Hainan Free Trade Port (FTP), making institutional arrangements for the construction of the Hainan FTP at the national legislative level. This came just one year after China released the roadmap that laid out a series of policies for Hainan to be transformed into a world-leading free trade hub like Hong Kong and Singapore.
The Hainan FPT comprises three chapters covering all the areas involved in the port’s construction, including the liberalization and facilitation of trade (1), investment (2) and taxation system (3).
- Liberalization and facilitation of trade
The Law guarantees to establish a special customs supervision zone system of Hainan FTP for independent customs operations throughout Hainan Island.
For cross-border trade in goods, Hainan FTP draws a distinction between a “first line” to overseas countries and a “second line” to the Chinese mainland:
- the first line will be open – goods (except those on Hainan’s prohibitive or restrictive lists) can be freely imported and exported between overseas regions and Hainan FTP under customs’ special supervision.
- the second line will be more tightly controlled – goods entering the Chinese mainland from Hainan will go through procedures in accordance with relevant import regulations, customs duties, and taxes.
2. Liberalization and facilitation of investment
Investment-wise, Hainan launches a simplified negative list for foreign investment and special measures for relaxing market access.
The negative list, implemented from February 1, 2021, expanded market access to foreign investment in various sectors, such as telecommunications, education, business services, manufacturing, and mining, in Hainan FTP.
3. Own tax system
The Law also supports Hainan FTP to establish its own taxation system based on the principles of “zero tariffs”, “low tax rates”, and “simplified tax regime”:
- Zero tariffs – After 2025, all goods imported from overseas will be exempt from import duties (except for those listed in the to-be-formulated Negative List). Before that time, some goods imported from overseas subject to one zero-tariffs negative list and three positive lists can be exempt from import duties, value-added tax (VAT), and consumption tax. For goods entering into Hainan FTP from the mainland, VAT and consumption tax that were levied can be refunded pursuant to the relevant provisions.
- Low tax rates – The Hainan FTP Law reiterates favourable corporate income tax (CIT) policies in Hainan, although it does not make specific provisions for tax rates. According to the masterplan, enterprises registered in Hainan and engaged in substantive business activities in encouraged industry sectors will be taxed at a reduced CIT rate of 15 % by 2025, compared with the normal rate of 25%. After 2025, this policy will be expanded to all industry sectors (except those on Hainan’s investment negative list).
- Simplified tax regime – The Law stipulates that indirect taxes and fees on Hainan Island, such as VAT, consumption tax, vehicle purchase tax as well as construction tax should be streamlined into one sales tax to be levied at the retail point of goods and services.
Domestic and foreign investors who are interested in setting up in Hainan can take full advantage of Hainan FTP’s preferential policies by evaluating how these can align with their own business development strategies.
The implementation of the Hainan FTP Law undoubtedly demonstrates China’s determination to open wider to the outside world, promote economic globalization and enhance the confidence of investors, especially foreign investors.